Genetics
Genetics
The trait inheritance process (parents to offspring) is called genetics. This includes:
The trait inheritance process (parents to offspring) is called genetics. This includes:
- the molecular structure and function of genes
- gene behaviour in the context of a cell or organism
- gene distribution
- variation and change in populations.
Genomics
Genomics is the study of an organism’s genome and the use of the genes (the genes of a cell, or tissue, at the DNA (genotype), mRNA (transcriptome), or protein (proteome) levels). Genomics deals with the systematic use of genome information, associated with other data. This is done in order to provide answers in biology, medicine and industry.
Genomics includes intensive efforts to determine the entire DNA sequence of organisms and fine-scale genetic mapping efforts. It also includes studies of intragenomic phenomena, such as heterosis, epistasis, pleiotropy and other interactions between loci and alleles within the genome.
The major tools and methods related to genomics are bioinformatics, genetic
analysis, measurement of gene expression, and determination of gene function. Such identified genes can be called major genes located at Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL). Although the term QTL strictly applies to genes of any effect, in practice it refers only to major genes, as only these will be large enough to be detected and mapped on the genome. Following the pattern of inheritance at such QTL might assist in selection.
Genomics is the study of an organism’s genome and the use of the genes (the genes of a cell, or tissue, at the DNA (genotype), mRNA (transcriptome), or protein (proteome) levels). Genomics deals with the systematic use of genome information, associated with other data. This is done in order to provide answers in biology, medicine and industry.
Genomics includes intensive efforts to determine the entire DNA sequence of organisms and fine-scale genetic mapping efforts. It also includes studies of intragenomic phenomena, such as heterosis, epistasis, pleiotropy and other interactions between loci and alleles within the genome.
The major tools and methods related to genomics are bioinformatics, genetic
analysis, measurement of gene expression, and determination of gene function. Such identified genes can be called major genes located at Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL). Although the term QTL strictly applies to genes of any effect, in practice it refers only to major genes, as only these will be large enough to be detected and mapped on the genome. Following the pattern of inheritance at such QTL might assist in selection.
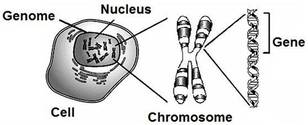
Cell structure
Cells are components of the body. In a cell the genome can be found. This includes nucleus, this contains chromosomes.
A chromosome holds a body's gene. A gene contains DNA. Almost all cells contain DNA - DNA is located in the cell nucleus (nuclear DNA), but some DNA can be found in the mitchondria (mitochondrial DNA).
Cells are components of the body. In a cell the genome can be found. This includes nucleus, this contains chromosomes.
A chromosome holds a body's gene. A gene contains DNA. Almost all cells contain DNA - DNA is located in the cell nucleus (nuclear DNA), but some DNA can be found in the mitchondria (mitochondrial DNA).
